BitAcross: A Trustless Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol for Bitcoin
BitAcross emerges as a groundbreaking protocol in blockchain technology, aiming to revolutionize the interoperability of assets on the Bitcoin network. It specifically addresses the challenge of limited liquidity for emerging assets, such as BRC-20 tokens. By forming a bridge between Bitcoin and various other blockchain networks, BitAcross enables the smooth transfer of assets while also significantly reducing transaction fees, a notable issue in conventional blockchain transactions.
Key Features
Innovative Combination of ZKP and TEE
At the core of BitAcross is the strategic integration of Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP) and Trusted Execution Environments (TEE). This combination is pivotal in facilitating trustless and efficient cross-chain transactions, thereby overcoming inherent risks and limitations associated with current methods of blockchain interoperability.
-
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP): ZKP plays a vital role in maintaining state integrity within the network. It allows the verification of state transitions in a trustless manner, ensuring the privacy and security of the transactions.
-
Trusted Execution Environments (TEE): TEE adds a crucial security layer to the protocol. It safeguards sensitive information, such as wallet details, and guarantees the execution of publicly agreed-upon logic. This ensures that the network remains secure and operations are transparent and tamper-proof.
Independent Sidechain for Enhanced Functionality
- BitAcross Network: This independent blockchain network, which supports EVM smart-contract, acts as the validated service layer where consensus is achieved. It provides the necessary security, data availability, and public auditability for the protocol. This Network is central to the protocol's functionality and security.
The protocol's versatility is showcased in its ability to build token bridges between Bitcoin and various blockchains, including Ethereum and Binance Smart Chain. Beyond facilitating asset transfers, BitAcross also lays the foundation for developing advanced layer 2 networks and trustless oracles on Bitcoin. This opens up possibilities for complex cross-chain applications such as credit systems and lending platforms, significantly broadening Bitcoin's functional reach.
By harnessing the synergistic power of ZKP and TEE, BitAcross sets a new standard in blockchain interoperability. The protocol not only addresses existing limitations in cross-chain asset transfers but also catalyzes the development of innovative applications, enhancing the overall utility and efficiency of the blockchain ecosystem.
Introduction to BitAcross
Background
The innovation of new token standard on Bitcoin like BRC-20 tokens is a response to the evolving blockchain landscape, where the demand for broader functionality and diverse financial instruments is constantly growing. One key driver for this innovation is the concept of "fair launch," which emphasizes equitable and transparent distribution methods for new assets. Coupled with the use of inscriptions, which embed additional data within Bitcoin transactions, these assets offer enhanced capabilities and richer features compared to traditional Bitcoin transactions. This evolution reflects a significant shift in the Bitcoin ecosystem, moving towards more complex and versatile applications that cater to a wider range of financial and technological needs.
Problem Statement
Despite the innovation and potential of the new token standard, their integration into the wider blockchain ecosystem from Bitcoin faces significant challenges. Since Bitcoin is not turing complete, the movement and utility of these assets is limited, these new assets struggle with liquidity issues due to their limited exposure and accessibility outside the Bitcoin network. hindering their potential for broader market adoption and reducing their effectiveness as financial instruments. So that a cross-chain interoperability solution is needed.
Current cross-chain interactions face challenges in terms of availability, centralization, and security. Many token bridge projects have suffered from security breaches, leading to substantial financial losses, as seen in the Wormhole and Nomad incidents. A contemporary solution involves deploying smart contracts on both chains to verify ZKPs, enhancing security and trust.
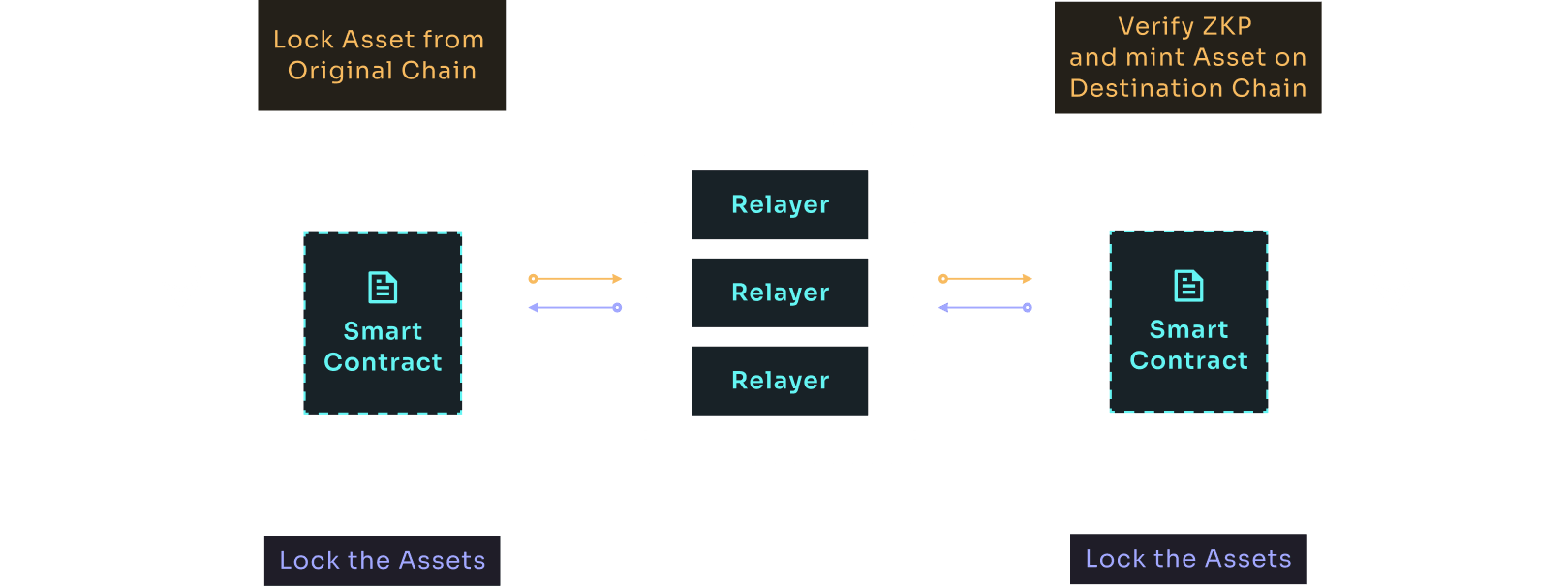
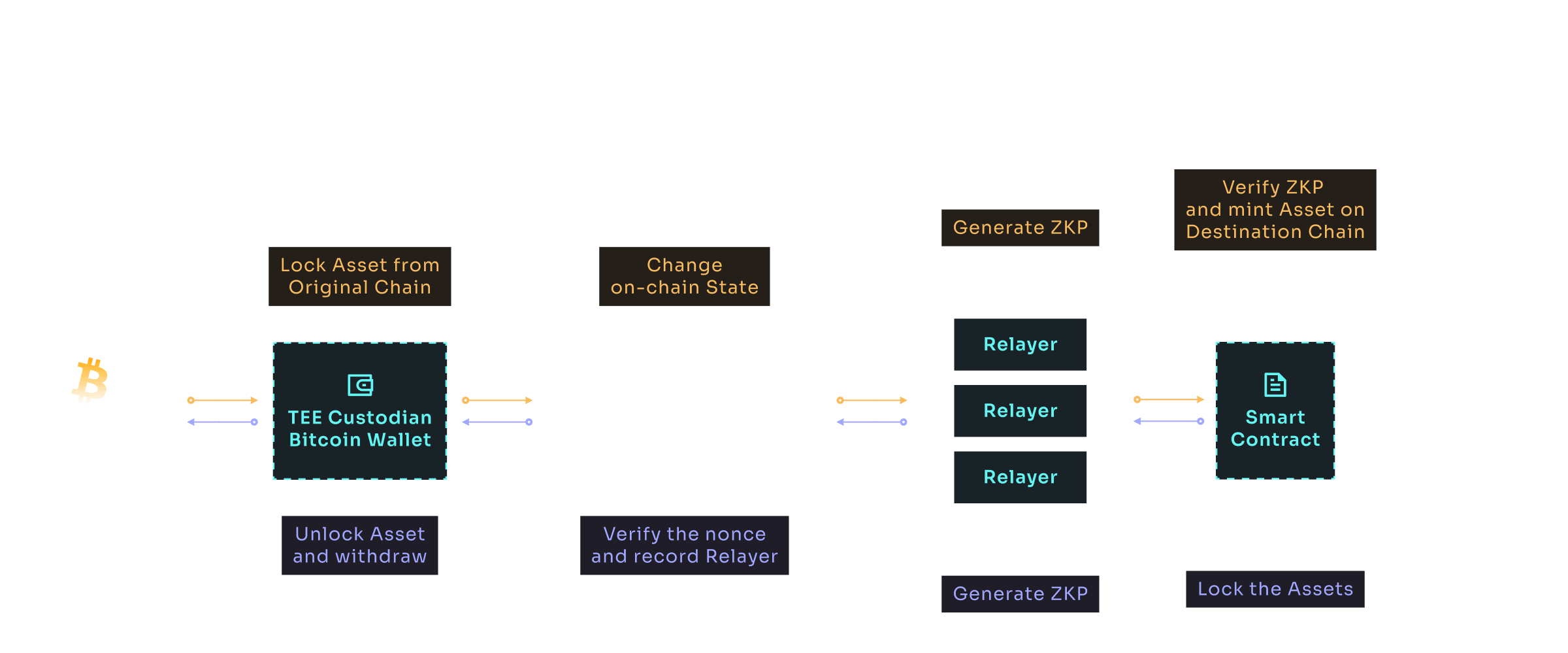
In the above diagram,
-
cross-chain message requests are sent to a designated smart contract on the original chain, where assets are locked.
-
Relayers sign the transaction and create state transition proofs using zero-knowledge techniques.
-
These proofs are submitted to the smart contract on the destination chain.
-
The destination chain's smart contract validates the ZKP and the transaction, then mints the corresponding assets.
-
Relayers gather data from the destination chain, create receipts in the form of ZKP, and record them on the original chain.
However, Bitcoin's limitations in running smart contracts pose a unique challenge for verifying ZKPs. Current Bitcoin cross-chain solutions, including MultiBit, face significant challenges predominantly in terms of centralization risks and audit and compliance hurdles. Centralization risks stem from the reliance on intermediaries or custodial services, which can become single points of failure and targets for attacks, compromising the security and integrity of cross-chain transactions.
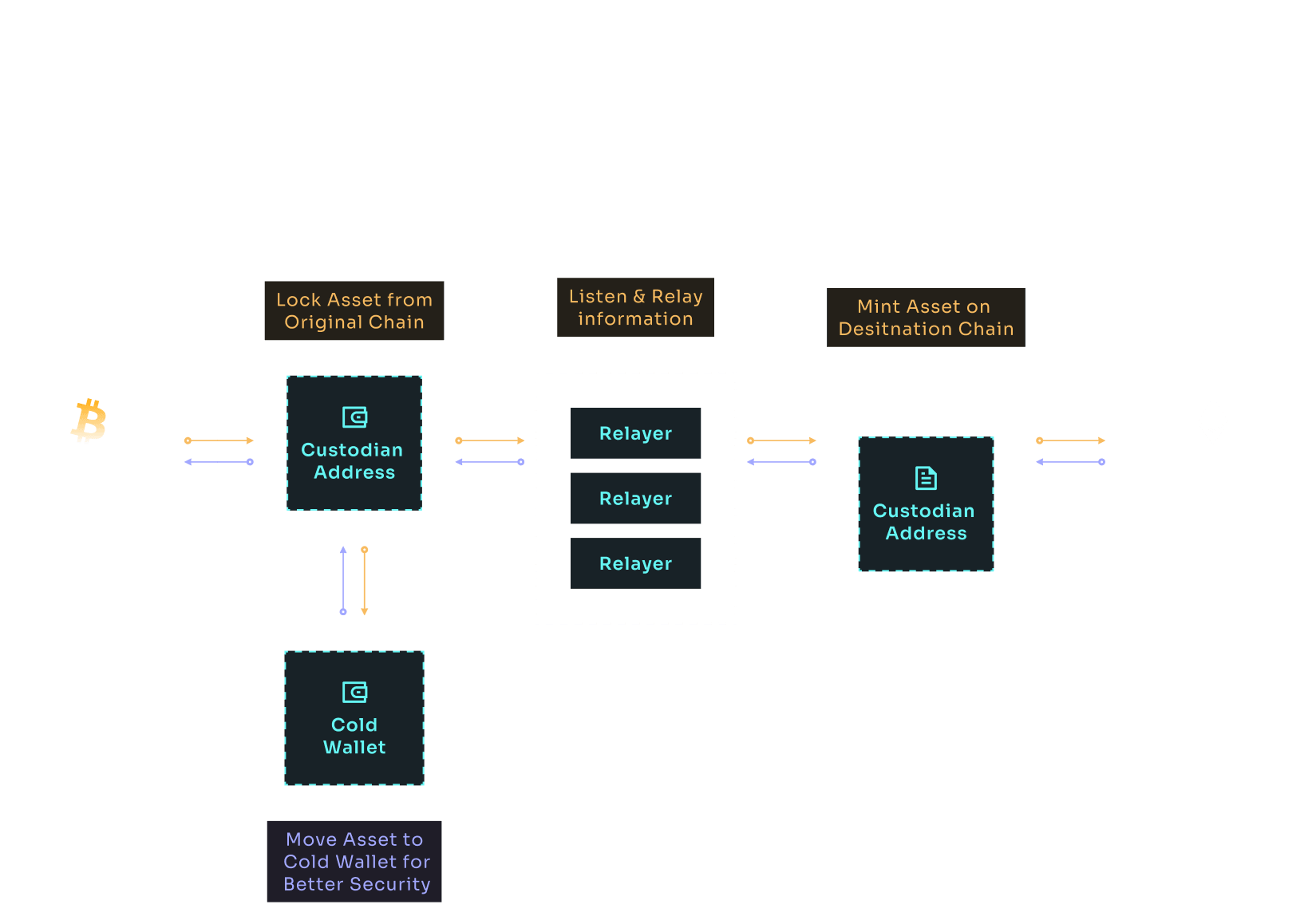
Proposed Solution: Enhancing Interoperability with BitAcross
BitAcross emerges as a groundbreaking solution to address the interoperability challenges faced by new Bitcoin-based assets like BRC-20 tokens. By enhancing cross-chain interactions, BitAcross aims to unlock the full potential of these assets, ensuring their accessibility and utility across various blockchain networks.
-
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP): The protocol employs Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP) to authenticate actions on the origin chain in a verifiable and trustless manner. By processing ZKPs through smart contracts on the destination chain, actions like token minting can be securely executed.
-
Trusted Execution Environments (TEE): TEEs provide a secure platform for transaction execution, safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring that all transactions adhere to the predefined logic.
-
Independent Network: The BitAcross network, supporting EVM smart contracts, is a vital component that offers security, data availability, and public auditability, ensuring the integrity and reliability of cross-chain transactions. This network is Turing-complete and supports the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), thereby overcoming Bitcoin's smart contract limitations and opening new avenues for blockchain interoperability and functionality.
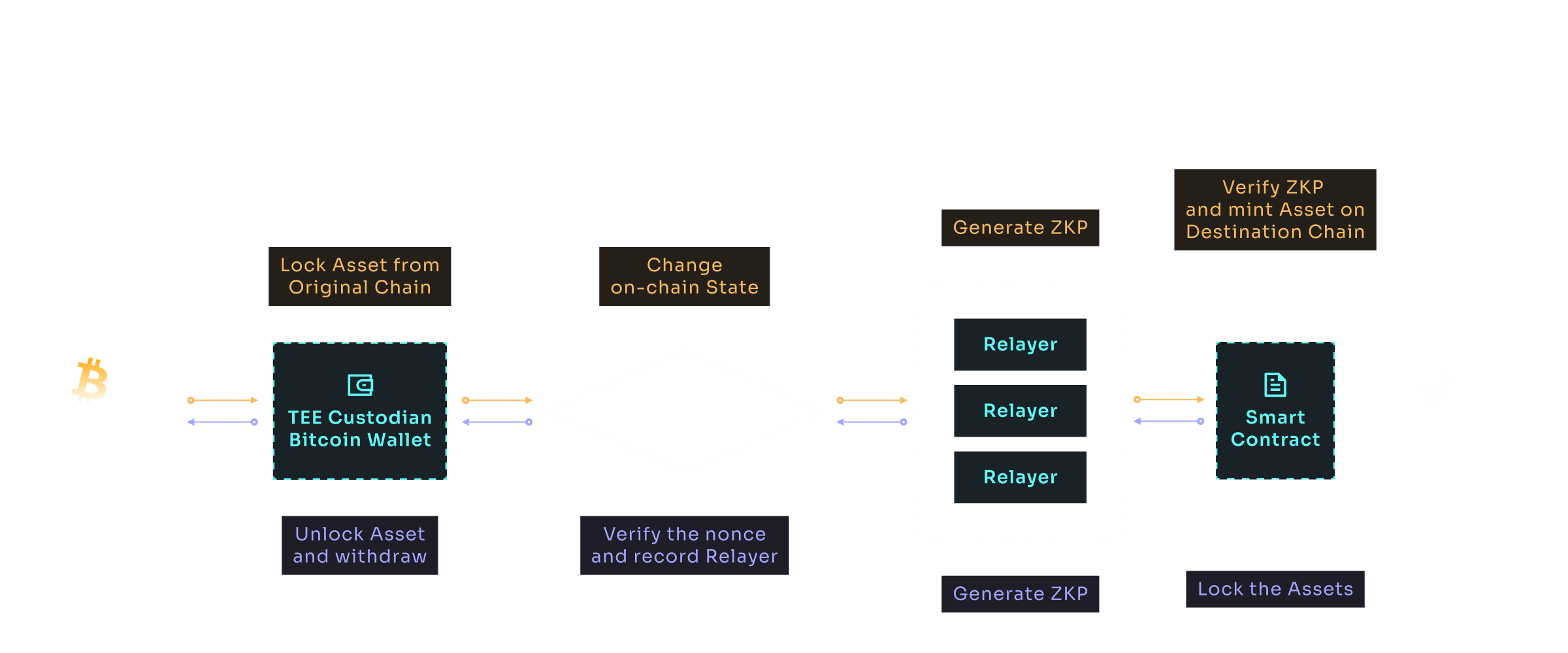
Through these innovative technologies, BitAcross not only enables the smooth transfer of BRC-20 and other Bitcoin-based assets to different blockchain networks but also paves the way for the development of advanced decentralized applications and financial platforms. This protocol plays a crucial role in enhancing the interoperability and liquidity of new assets on the Bitcoin network, marking a significant advancement in the blockchain ecosystem.
Architecture
The BitAcross protocol is built to ensure security, decentralization, and efficient cross-chain communication, leveraging advanced technologies like Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP) and Trusted Execution Environments (TEE). Here's an overview of its key components:
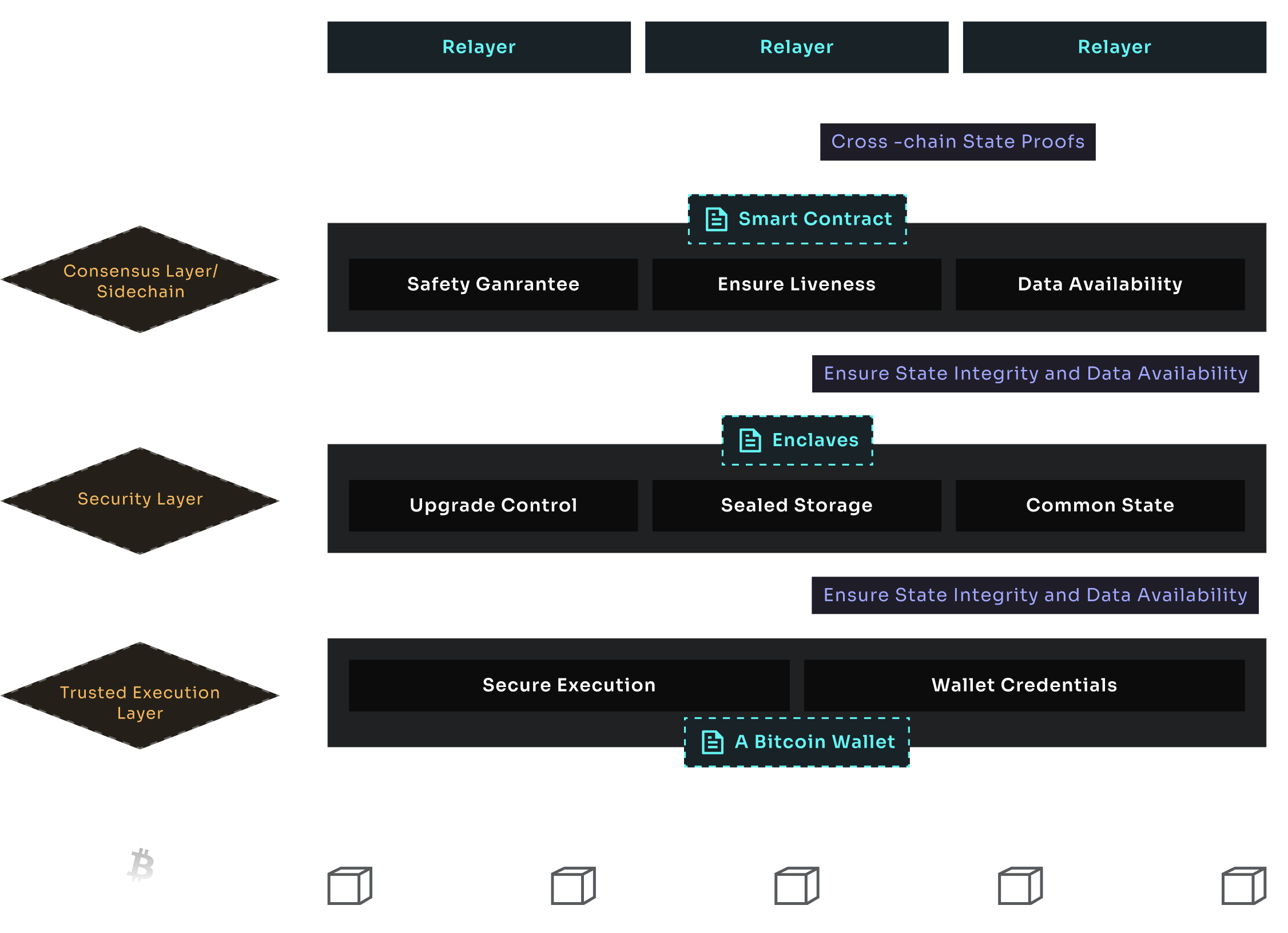
BitAcross Network
The BitAcross network forms the backbone of the protocol, providing a secure and decentralized platform for transactions.
Consensus Layer
The consensus Layer composed of nodes that ensure public auditability and data integrity. It supports Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) smart contracts, thereby facilitating versatile blockchain applications. Its design guarantees that the protocol remains live and functional without centralized control, ensuring that transactions and state updates comply with the application logic.
Security Layer
Operating under the consensus of the BitAcross network, the security layer is crucial for safeguarding sensitive data. It comprises TEE enclaves that securely store information and require consensus from the BitAcross network for any logic updates. This decentralized operation ensures a robust and tamper-resistant security infrastructure.
Trusted Execution Layer
This layer includes a Bitcoin vault that can processes transactions on the Bitcoin network. It operates under the directives of TEE nodes in the security layer, with credentials for the Bitcoin vault decentralized and protected by the security layer. The use of cold wallets for PSBT and multi-signature signing adds an extra layer of security for transactions.
Relayers
The permissionless Relayers plays a vital role in ensuring the finality and integrity of cross-chain transactions. It uses ZK proofs to relay messages and transaction information between the original and destination chains. Relayers, functioning similarly to validators in other blockchains, maintain light clients of both chains to facilitate this process. Then are incentivized by part of the transaction fees and are bind with mechanisms to penalize relayers for delays or inaccuracies in submitting proofs.
This architecture positions the BitAcross protocol as a cutting-edge solution in the realm of blockchain interoperability, particularly for Bitcoin-based assets, addressing key challenges of security, decentralization, and cross-chain transaction efficiency.
Consensus Layer
The consensus is a foundational component of the BitAcross network, designed to enhance the interoperability and liquidity of Bitcoin-based assets like BRC-20 tokens. This consensus Layer plays a pivotal role in ensuring both public auditability and maintaining robust security within the network. Here are the key functionalities and features of the consensus layer:
-
Node Composition: The consensus layer is composed of multiple nodes, which work together to maintain the network's integrity and performance. These nodes are responsible for processing transactions, maintaining the blockchain, and ensuring the network's overall health and efficiency.
-
Decentralized Attestation for TEE Nodes: It provides remote and decentralized attestation for Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) Nodes. This feature is crucial for verifying the integrity and security of the TEE nodes, ensuring they operate correctly and securely.
-
Public Auditability: The consensus layer offers public auditability for all registered information and transaction data. This transparency is key to maintaining trust among users and for the verification of transactions and state changes on the network.
-
Data Availability Layer: Serving as the data availability layer, the BitAcross consensus layer ensures that all transactions and state transitions are agreed upon by the network nodes, thereby maintaining the blockchain's consistency and reliability.
-
Governance and Enclave Upgrade Logic: The consensus layer incorporates governance mechanisms to manage and initiate upgrades to the network, particularly regarding the enclave logic. This governance ensures that changes to the network are made democratically and in line with the community or stakeholders' consensus.
-
Support for EVM Smart Contracts: One of the critical features of the consensus layer is its support for Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) smart contracts. This allows for a wide range of applications and functionalities to be built and executed on the consensus layer, expanding its use cases beyond simple asset transfers.
-
State Update and Execution Integrity: The network is designed to ensure that the state is only updated, and execution proceeds strictly in accordance with the predefined application logic. This feature is vital for maintaining the correctness and predictability of the network's operations.
-
Protocol Liveness: The design of the BitAcross consensus layer ensures the continuous operation of the protocol, preventing it from being halted or disrupted by any single party. This resilience is crucial for maintaining the network's availability and reliability.
Overall, the BitAcross consensus layer is engineered to provide a secure, transparent, and efficient platform for cross-chain interactions, particularly focusing on enhancing the capabilities of Bitcoin-based assets in the broader blockchain ecosystem.
Security Layer
The Security Layer of the BitAcross Network is a critical component designed to safeguard the network and its transactions, operating under the consensus of the Zero-Knowledge (ZK) network. This layer is pivotal in maintaining the integrity and security of the protocol, especially for Bitcoin-based assets like BRC-20 tokens. Here are the key aspects of the Security Layer:
-
Composition of TEE Enclaves: The Security Layer is composed of Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) enclaves. TEEs are specialized secure areas of a processor that provide an isolated execution environment. They ensure that the code and data loaded inside the enclave are protected with respect to confidentiality and integrity.
-
Storage of Sealed Information: One of the primary functions of the TEE enclaves in the Security Layer is to securely store sealed information. This includes sensitive data that needs protection from external threats and unauthorized access, ensuring that only authenticated and authorized entities can access or modify it.
-
Consensus Requirement for Logic Updates: Any updates to the logic or protocols within the TEE enclaves require a consensus from all the TEE enclaves within the network. This mechanism ensures that no single enclave can unilaterally make changes, thereby maintaining a decentralized control structure. This requirement for a unanimous consensus enhances the security and stability of the protocol.
-
Decentralized Operation and Maintenance: The TEE enclaves are operated and maintained in a decentralized manner. This decentralization is further strengthened as the maintenance responsibility is distributed among leading industrial projects. This approach ensures that no single entity or party has complete control over the Security Layer, mitigating the risks associated with centralization.
-
Authority for Authorizing Key Generation: In cases where the logic needs to be updated, the authority to generate an authorization key is vested in the collective consensus of the TEE enclaves. This process requires coordination and agreement among all enclaves, ensuring that any changes to the system are thoroughly vetted and agreed upon by the network.
The Security Layer's design in the BitAcross protocol plays a vital role in ensuring the robustness and resilience of cross-chain transactions. By leveraging the advanced capabilities of TEE enclaves and maintaining a decentralized governance structure, the Security Layer provides a solid foundation for secure and efficient blockchain interoperability.
Trusted Execution Layer
The Trusted Execution Layer is an integral part of the BitAcross protocol, designed to enhance the security and efficiency of transactions within the Bitcoin network. This layer plays a pivotal role in managing and executing transactions, particularly for Bitcoin-based assets like BRC-20 tokens. Here are the key components and functionalities of the Trusted Execution Layer:
-
Bitcoin Vault Management: The layer features a Bitcoin vault that is pivotal in processing transactions on the Bitcoin network. This vault acts as a secure storage for Bitcoin assets, ensuring their safety and accessibility for authorized transactions.
-
Controlled Execution by TEE Nodes: The execution of transactions and operations within this layer is exclusively controlled by the commands issued from the TEE nodes in the Security Layer. This setup ensures that all actions undertaken in the Trusted Execution Layer are secure, authenticated, and comply with the protocol's overall security guidelines.
-
Decentralized Credential Management: The credentials for accessing the Bitcoin vault are generated and maintained in a decentralized manner by different enclaves within the Security Layer. This decentralization is crucial for preventing single points of failure and for enhancing the overall security of the vault.
-
Integrity and Availability of the Bitcoin Wallet: The Security Layer plays a significant role in ensuring the integrity and availability of the Bitcoin wallet associated with the vault. By safeguarding the wallet credentials and overseeing access, the Security Layer ensures that the wallet remains secure and functional at all times.
-
Approval Process for Credential Updates: Any updates or changes to the Bitcoin credentials require approval from the nodes within the Security Layer. This process ensures that any modifications to the access credentials are collectively agreed upon, maintaining a high level of security and consensus within the network.
-
Enhanced Security with Cold Wallets: To further boost security, the Trusted Execution Layer incorporates the use of cold wallets for multi-signature signing with Partially Signed Bitcoin Transactions (PSBT). Cold wallets, being offline storage, provide an additional layer of security against online threats, while multi-signature signing ensures that transactions are authorized by multiple parties, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or fraudulent activities.
The Trusted Execution Layer, with its advanced security measures and controlled execution protocols, plays a crucial role in the BitAcross protocol. It ensures that Bitcoin transactions are processed securely and efficiently, adhering to the highest standards of security and trust, essential for the successful operation of cross-chain functionalities in the blockchain ecosystem.
Relayers
Relayers constitute a critical component of the BitAcross protocol, ensuring the seamless and secure finality of cross-chain transactions. They play a pivotal role in bridging the gap between different blockchain networks, such as Bitcoin and other chains, using advanced cryptographic techniques. Here are the key functions and characteristics of relayers within the BitAcross ecosystem:
-
Finality Assurance with Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs): Relayers use ZKPs to guarantee the absolute finality of cross-chain transactions. ZKPs provide a way to prove the validity of transactions without revealing any sensitive information, thereby enhancing privacy and security.
-
Maintenance of Light Clients: Relayers are responsible for maintaining light clients for both the original chain (e.g., Bitcoin) and the destination chain. This involves keeping essential data that is necessary for processing and verifying cross-chain transactions.
-
Transaction Information Packaging: These relayers aggregate transaction information into blocks and generate ZKPs using the corresponding circuit. This process is crucial for ensuring that the transaction data is accurate and securely transmitted between chains.
-
Validation and Settlement Proposals: Once the ZKP is generated, it is the responsibility of validators on the destination chain to verify its validity. If the ZKP is confirmed as valid, validators on the destination chain proceed with proposing settlements based on this information.
-
Role Similar to Validators: Relayers function in a capacity similar to validators in traditional blockchain networks. However, they do not bear the same burden of providing security guarantees, as this is managed by the robustness of the ZKP mechanism. If a ZKP turns out to be invalid, the corresponding transaction is halted by the smart contract on the destination chain, ensuring the integrity of the process.
-
Transaction Relay Between Chains: Relayers are tasked with relaying transaction information back and forth between the original and destination chains. This continuous communication is vital for maintaining a consistent and up-to-date state across different blockchain networks.
-
Proof Submission Mechanism: The network allows relayers to agree on a proof submission mechanism. This determines who among the relayers is responsible for creating and submitting new proofs. This flexibility is crucial for maintaining an efficient and responsive relay system.
-
Incentive Mechanism: The BitAcross protocol envisages an incentive mechanism for relayers. This is designed to motivate and reward them for their crucial role in managing and securing cross-chain transactions.
In summary, relayers in the BitAcross protocol are essential for facilitating secure, efficient, and reliable cross-chain interactions. By leveraging ZKPs and maintaining light clients of involved blockchains, they ensure that cross-chain transactions are not only possible but also carried out with the highest standards of security and efficiency.
Applications of the BitAcross Protocol
The BitAcross protocol, with its innovative architecture and advanced functionalities, opens up a wide range of applications in the blockchain ecosystem. These applications leverage the protocol's ability to facilitate secure, efficient, and trustless cross-chain transactions. Key applications include:
Token Bridge
- BRC-20 Asset Integration: The protocol enables the creation of a token bridge that connects Bitcoin and other Turing-complete blockchains. This bridge allows for the trustless transfer of new standard token on Bitcoin, across different blockchain networks. Users can thus interact with BRC-20 assets on platforms that traditionally would not support Bitcoin-native tokens.
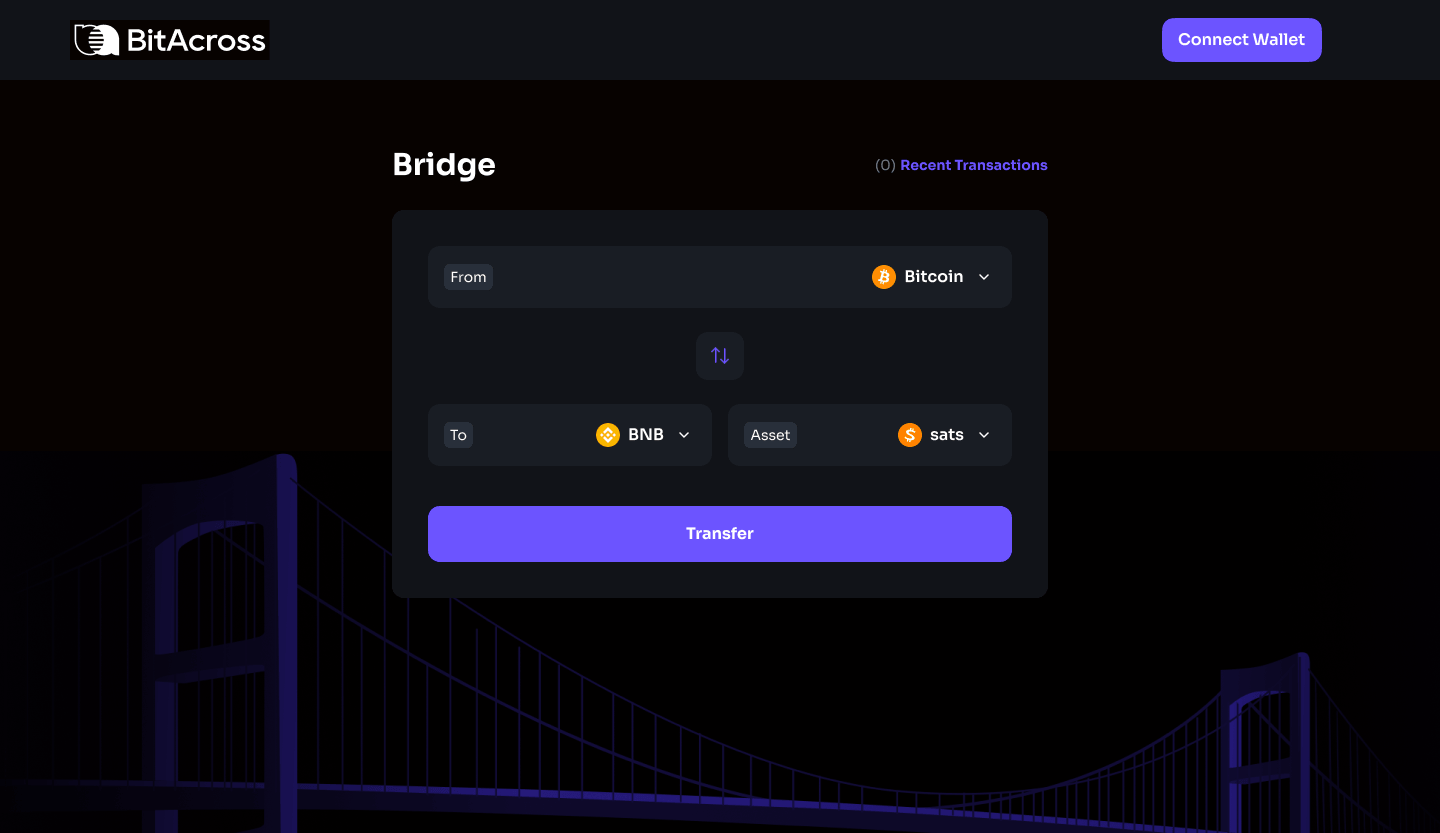
This is a sample token bridge working in progress
Automated Market Maker (AMM) Decentralized Exchange (DEX)
By integrating with AMM-based decentralized exchanges, the BitAcross protocol can significantly improve liquidity and trading opportunities for Bitcoin-based assets. It allows for the creation of liquidity pools and trading pairs involving BRC-20 tokens and other cryptocurrencies, facilitating decentralized and trustless trading across different blockchains.
Cross-Chain Oracle
The protocol can be used to develop cross-chain oracles, which are essential in providing accurate and real-time data from various blockchains to smart contracts. This capability is crucial for decentralized applications that rely on external data, such as price feeds, for their operations.
Cross-Chain Credit System with Ordinal NFTs
Utilizing the unique features of Ordinal NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens), the BitAcross protocol can establish a cross-chain credit system. In this system, users can debit an Ordinal NFT on one chain and then withdraw tokens on another chain. This functionality opens up new possibilities for decentralized finance (DeFi), allowing for more flexible and innovative credit and lending solutions that operate across multiple blockchains.
Each of these applications demonstrates the versatility and transformative potential of the BitAcross protocol in bridging the gaps between Bitcoin and other blockchain networks. By enabling a wide range of cross-chain functionalities, the protocol paves the way for a more interconnected and efficient blockchain ecosystem, expanding the use cases and reach of Bitcoin-based assets.